Let’s start by looking at the history of hybrid vehicle development, consider the classification of hybrids, and their advantages and disadvantages.
The history of hybrid vehicle development
The first, simple and slow, hybrid self-propelled units since these machines can hardly be called cars appeared in the 19th century. Unlike modern ones, “hybrid” vehicles of that time were driven by the power of water vapor and the maximum speed of such a system on the wheels did not exceed ten kilometers per hour.
The very very first car to use electrical energy as a driving force was designed in 1839 by the Scotsman Robert Anderson. Unfortunately, at that time no one paid attention to his invention.
Lohner Electric Chaise/Lohner-Porsche Mixte Voiturette
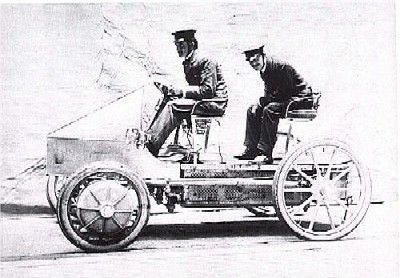
50 years later, at the turn of the century, two more people entered their names into the annals of the evolution of hybrid cars: the Belgian Henri Pieper, who in 1905 patented a hybrid scheme for a car which provided for the use of an electric motor along with a gasoline one and the German Ferdinand Porsche, who owns the history of the creation of the second car Lohner Electric Chaise or Lohner-Porsche Mixte Voiturette. His hybrid car was built in 1899.
The system, called the Lohner-Porsche Mixte, used a gasoline engine to power the electric motors that powered the car’s front wheels. The Lohner Electric Chaise, a front-wheel-drive petrol-electric vehicle based on the Lohner-Porsche electric car, was well received at the 1901 Paris Motor Show.
There are several versions of how to set in motion a hybrid Lohner Electric Chaise. In one of them, the car moved thanks to the coordinated work of electric motors and an internal combustion engine with a generator that generates electricity, in the other – it worked using the energy of a massive 44-cell battery. On a single charge, the Chaise car could travel up to 65 kilometers.
Of course, producing such cars with their economy and environmental friendliness was very expensive at that time so cheaper classic cars and Henry Ford’s conveyor revolution supplanted innovative developments of designers.
The first full hybrid drive system
In 1968, TRW company engineers created the first full hybrid drive system used in modern cars today. In 1973, the German company Volkswagen presented its Volkswagen Taxi Hybrid to the public. In 1976, the United States Congress passed the Electric and Hybrid Vehicle Research, Development and Demonstration Act to reduce air pollution from automobile emissions.
This gave the government incentives to develop electric vehicles in the United States. Toyota’s press service released the data on the company’s intentions to seriously engage in the development of the most economical vehicles with low pollution rates.
Toyota Prius enters the hybrid industry
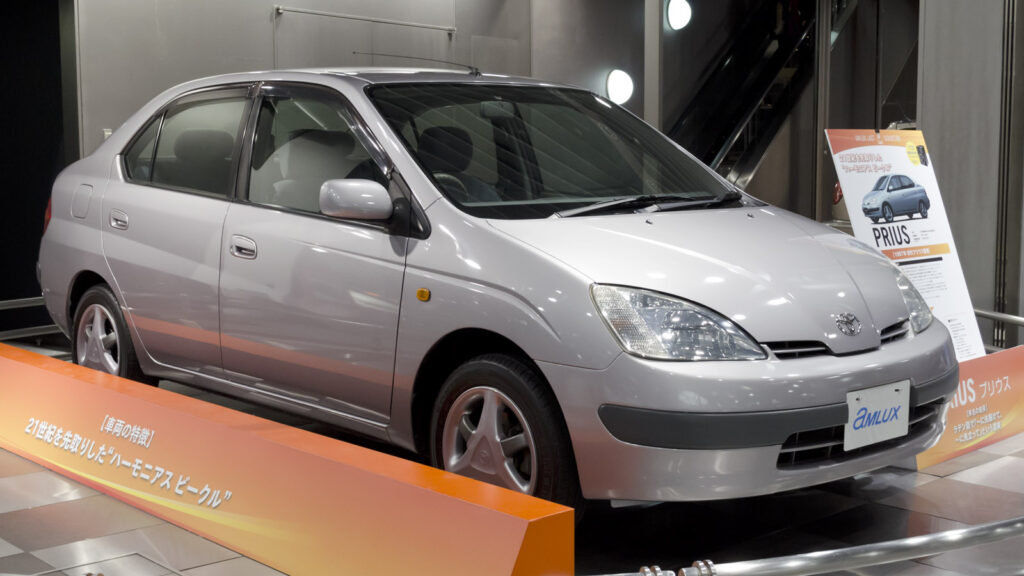

In 1997 Toyota Prius entered the Japanese market, which can now be called the symbols of modern hybridization With the beginning of the new millennium, Toyota began shipping the Prius overseas. The United States is one of the most successful marketplaces for hybrid vehicles in the world.
Despite the brilliant success, there were some unpleasant incidents. In 2005, Toyota officially announced the recall of 160,000 Prius hybrids for repair. The problem was a software failure in the car’s computer, which often led to a sudden stop of the gasoline engine while driving.
Undoubtedly, Toyota, as before, continues to lead in terms of the volume of hybrids produced annually, but SUVs Lexus RX 400h and Lexus LS 600h have already taken significant positions in the market. Also, among the most successful and profitable hybrid cars over the past few years, We would classify the Chevrolet Volt, Ford Escape Hybrid.
We think this is where we can finish reviewing the history of the development of hybrids and move on. So, an electric hybrid is a car driven by an internal combustion engine and a traction motor. At the present stage, electric hybrids are classified according to several criteria. Depending on what role the electric machine plays in the power plant, hybrids are divided into assisted (or micro) hybrids, mild hybrids, and full hybrids also there is a hybrid with a range extender and plug-in hybrid.
Types of hybrids and their main features
Since we have already considered this classification, now we will quickly repeat the main types of hybrids and their main features.
- Assisted hybrid (Micro hybrid): the electric car implements the Start-Stop and braking energy recovery systems.
- Mild hybrid: the electric motor serves as an assistant to the internal combustion engine in running start and acceleration modes,
- Full hybrid: the electric drive provides limited autonomous electric driving mode.
- Micro-hybrids usually use a resident (internal) voltage of 12 V, and the electric machine that is generated has low power. In such systems, a dual-use reversible electric machine (dinostarter) can be used.
- The mild-hybrid has a battery of relatively small capacity and an electric motor of limited power, which is activated when the car accelerates along with the operation of the main internal combustion engine.
- Mild hybrids can use heightened 36 V, 42 V, or high 300 or 700V voltage drive systems. At the same time, the composition of the hybrid drive provides for parallel or series addition of the torques of alternative engines series or parallel scheme for constructing a hybrid power plant.
- A full hybrid is characterized by a high drive voltage and significant traction motor power. For this, the system uses a powerful high-voltage traction battery.
- In full hybrids, traction battery charging devices from external sources are used to increase the autonomous run on electric traction These cars have received the “plug-in” status.
You may also like to read: Electric Vehicle Classification
A compromise scheme of the active Start-Stop system is possible, in which electric traction is used only in the mode of short-term movements at low speed driving in a traffic jam due to the electric starter.
The main disadvantage of this solution is the significant energy consumption of the starter motor in starting modes. The problem can be solved by using an electric valve or pneumatic starter machines. In the latter case, the car has maximum efficiency and torque at the minimum vehicle speeds.
Advantages and disadvantages of hybrid vehicles. (Pros and Cons)
Hybrid vehicle pros
- Environmental friendliness: One of the main reasons why public and private organizations are switching to hybrid vehicles is because they run on green sources. That is, CO2 emissions into the environment are significantly reduced during the operation of a hybrid vehicle Next one is the profitability. To promote hybrid vehicles, governments in many countries provide several loans for those looking to switch to a hybrid alternative. They are also subject to exemption from road tolls and significantly fewer tax payments annually in addition to low fuel costs, i.e. the electric motor and the internal combustion engine reduce fuel consumption when working together, saving the budget on average by 30-35%.
- Less dependence on fossil fuels: With an electric motor, a hybrid vehicle needs fewer fossil fuels, resulting in both lower emissions and less dependence on fossil fuels. Lower fuel prices can also be expected due to this. But the cost of electricity may rise.
- Regenerative braking system: The interesting thing about hybrid cars is that every time you apply the brakes while driving, the electric battery recharges a little.
- Higher resale value: As gasoline becomes more expensive more and more people switch to hybrid vehicles. This has led to a significant increase in the resale value of such vehicles. If you switch to a hybrid vehicle and are not satisfied with it, you can always resell it to someone looking for a similar vehicle and get a pretty high price tag.
Hybrid vehicles cons
- Less power: Hybrid cars use two independent engines, with the internal combustion engine serving as the main source of energy. The two engines in the car mean that neither the internal combustion engine nor the electric motor will be as powerful as in conventional gasoline or electric vehicles. The result is less power, which makes the cars unsuitable for dynamic acceleration.
- Expensive price tag: The first deterrent for many people is the high cost of hybrid cars, which is several thousand dollars more than that of conventional cars. However, this one-time investment will pay off over time.
- Difficult to handle: Hybrid cars have more nodes than conventional cars. This translates into more vehicle weight. The extra weight in vehicles reduces fuel efficiency. Therefore, hybrids have to compromise and reduce the engine size and battery capacity, consequently reducing the size of the battery.
- High maintenance costs: These vehicles can be expensive and difficult to repair and maintain due to the presence of two different types of engines electric motor and internal combustion engine Since the use of hybrid vehicles as consumer vehicles is fairly new, finding qualified service can be challenging.
- Battery replacement: Battery replacement of hybrid vehicles is currently rare. However, if a battery needs to be replaced, it can get pricey.
So today, we briefly reviewed the history and types of hybrids, their advantages, and disadvantages. We hope that everything was simple and clear. In case you have any questions, you can ask them in the comment section below.



